Password security: How to create strong passwords in 5 steps
Getting cyber smart starts with cyber hygiene. Here are tips and strategies to help keep you and your family Cyber Safe.

If you look back on the first time you created a password — be it for an email account or social media platform — you were probably told to think of a unique and complex password to help protect your information. Password security has always been relevant, but it has become even more so today as cybercriminals continue to think of new and innovative ways to hack accounts and get ahold of your personal data.
To this end, online users also need to follow new and innovative ways to create strong passwords that will keep their personal information protected. That’s where this complete guide to password security comes in. We’ll cover frequently asked questions, such as “How do I create a strong password?,” “Why is password security important?,” and “How does a password get hacked?” In addition, you’ll find how stolen passwords have recently affected businesses and individuals, along with password security tips that will help you live a more Cyber Safe lifestyle.
How to create a strong password
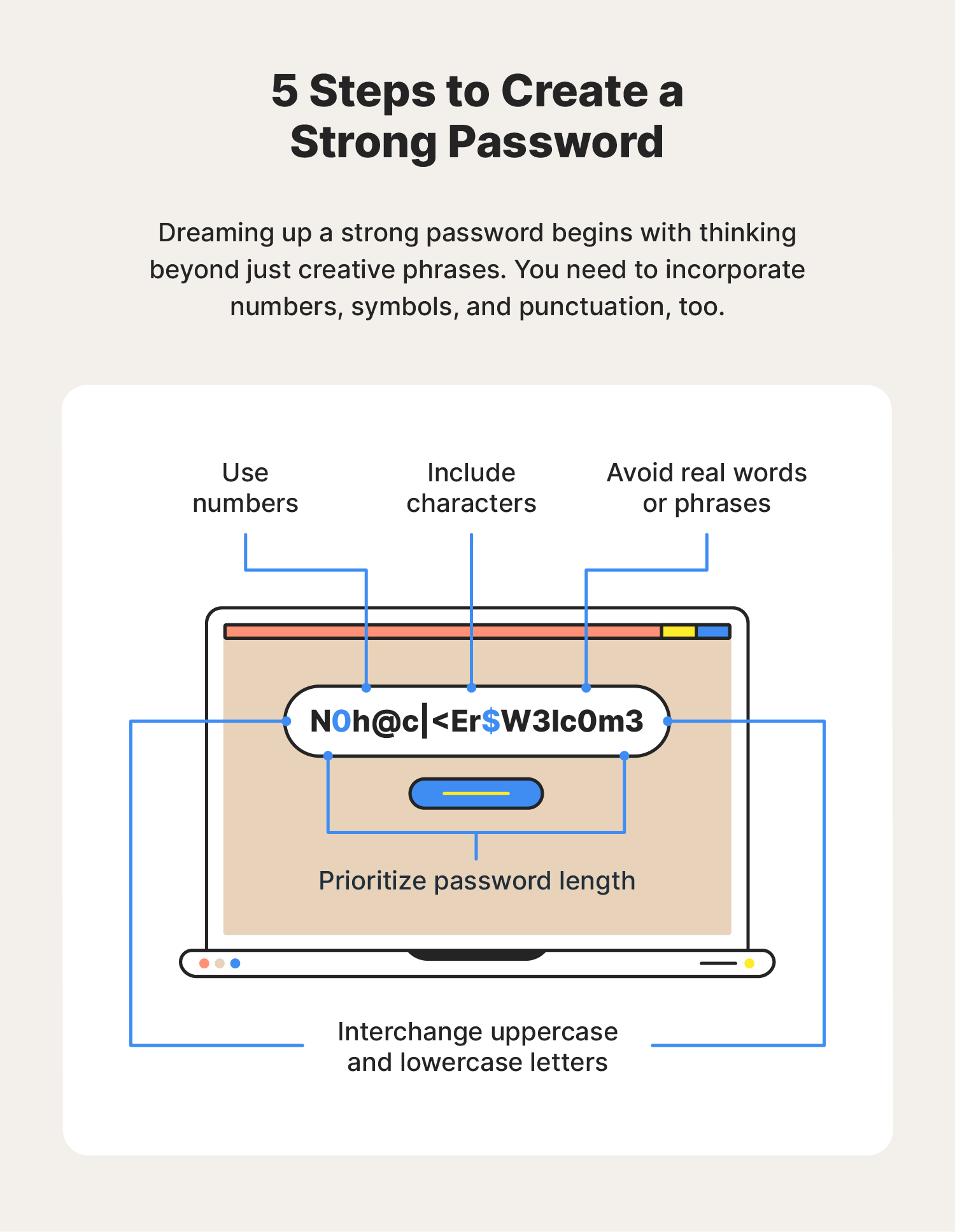
Living in the 21st century means knowing that the words “password” and “security” go hand in hand. In order to keep your accounts, information, and devices Cyber Safe, you'll need to know how to create a strong password. But you may be asking yourself, “What is a good password?”
Here are instructions on how to create a strong password that you can rely on:
- Never use personal information: Strong passwords shouldn’t include references to personal information such as names, birthdays, addresses, or phone numbers.
- Include a combination of letters, numbers, and symbols: Secure passwords include a variety of random characters, numbers, and letters to make the password more complex.
- Prioritize password length: Safe passwords should be at least 16 characters long to lessen the chances of falling victim to a data breach or cyberattack.
- Never repeat passwords: Reusing the same password for different accounts puts you at risk of credential stuffing attacks frequently used by cybercriminals.
- Avoid using real words: Hackers use malicious programs that can process every word found in a dictionary to crack passwords. Stay away from using proper nouns and other standalone dictionary words that could lead to an unsecure password.
Why is password security important?
On average, people reuse the same password for 10 different accounts. Because of this, it's needless to note that the majority of people need to rethink their password security.
Without having password security best practices top of mind, individuals and businesses alike could be leaving themselves open to cybersecurity threats. Some potential consequences of weak password security include:
- Data breaches
- Identity theft
- Computer hijacking
- Blackmail
- Loss of privacy
Inadequate password security could not only endanger the Cyber Safety of individuals and customers, but also could lead to financial troubles. Cybercriminals are often looking for ways to access personal banking information or use ransomware to make themselves a profit. Businesses and individuals within the U.S. lost nearly $4.2 billion to cybercrimes within the last year alone.
How does a password get hacked?

There are many ways for cybercriminals to hack the security passwords you took the time to dream up. Here’s a list of a few commonly used techniques to look out for.
Dictionary attacks
Dictionary attacks are a type of brute force cyberattack. Hackers use malicious programs to scan and test every word within a dictionary as a person’s password. These types of cyberattacks are why we emphasize the use of different letters, numbers, and symbols when creating secure passwords.
- PASSWORD SECURITY TIP: Avoid real words and incorporate a variety of letters, numbers, and characters.
Phishing scams
Phishing is a type of social engineering scam that tries to trick users into supplying their login credentials online. Hackers use malicious links and cloned websites to imitate legitimate businesses, presenting a fake form to input your login information.
- PASSWORD SECURITY TIP: Always check the links you’re clicking on and take advantage of antivirus software.
Password spraying
Password spraying is a hacking technique that cybercriminals use to guess the passwords of their potential victims. The method uses an extensive list of frequently chosen passwords to test against an individual’s username. If there is a match, the hacker will get access to the account information.
The remedy for this type of cyberattack falls back on creating strong, unique passwords and avoiding easy-to-remember phrases, which makes password spraying incredibly difficult for the cybercriminals at large.
- PASSWORD SECURITY TIP: Don’t fall back on commonly used passwords, such as “12345” or “qwerty.”
Keylogging
Keylogging involves the installation of malware that can track a person’s keystrokes as they type on their computer. Though these attacks are more difficult to pull off compared to phishing and password spraying attacks, it could lead to a hacker figuring out usernames and passwords if they pay enough attention.
Because the attacker is able to see what you’re typing, creating a strong password really won’t do anything to protect you. In this case, it’s a good idea to have cybersecurity software installed that can alert you of a potential threat on your device.
- PASSWORD SECURITY TIP: Explore antivirus software you can have installed onto your device.
Credential stuffing attacks
Not to be confused with password spraying, credential stuffing uses known passwords to gain access to account information. This differs from password spraying because the passwords tested during credential stuffing attacks are stolen credentials obtained in a previous data breach.
Protecting yourself against credential stuffing mainly involves remembering to never reuse the same passwords for different accounts — no matter how unique it may seem. This endangers your most sensitive data, which could put you in an undesirable situation.
- PASSWORD SECURITY TIP: Create unique passwords for each of your online accounts.
The effects of stolen passwords
To help you understand the true danger of not knowing how secure your passwords are, consider these recent statistics underscoring how relevant password security really is.
Individuals and stolen password consequences:
- 4 out of 10 people have had their data compromised online. (Google, 2019)
- There were over 240,00 phishing scam complaints reported in 2020. (FBI, 2020)
- 80 percent of data breaches involving hacking are connected to passwords. (Verizon, 2020)
- 63 percent of consumers fear their identity will be stolen. (Norton, 2021)
Businesses and stolen password consequences:
- Across all industries, it took 280 days on average to identify and contain a data breach. (IBM, 2020)
- 59 percent of U.S. consumers are likely to avoid businesses that have become a victim of a cyberattack within the past year. (Arcserve, 2020)
- 57 percent of all companies have experienced a mobile phishing incident. (Wandera, 2020)
- 68 percent of business leaders feel their risk of experiencing a cyberattack is increasing. (Accenture, 2019)
10 password security tips

Now that you understand the importance of password security and how to make strong passwords, pore over this full list of password security tips to improve your cyber hygiene.
- Don’t use personal information: Using names, birthdays, addresses, or phone numbers in your password could jeopardize its effectiveness against cyberattacks.
- Randomize patterns and sequences: Randomizing the patterns and sequences of letters, numbers, and characters can protect you against password spraying attacks.
- Never reuse passwords: Recycling old passwords leaves your accounts vulnerable to credential stuffing
efforts made by lurking cybercriminals. - Prioritize password length: The longer your password, the more difficult it will be for hackers to guess.
- Never share your passwords: Sharing your passwords with friends or family compromises the Cyber Safety of your personal accounts.
- Avoid public Wi-Fi: Using public Wi-Fi without a VPN allows hackers to track your online presence and potentially expose your device’s data, including saved credentials.
- Use a variety of numbers, letters, and characters: Hackers are less likely to gain access to accounts with complex passwords incorporating a variety of numbers, letters, and characters.
- Download a trusted password manager: Password managers are an excellent tool for people struggling to ideate and organize their own passwords.
- Check your password strength: Password strength checkers , like LastPass, allow people to validate the effectiveness of the password they created.
- Change passwords periodically: Switching up the passwords you created for your different accounts can reassure you that you’re taking all the necessary steps to keep your accounts and data safe.
Password security is important, but it’s only one part of your cybersecurity puzzle. To create a reliable cybersecure ecosystem for yourself, you’ll want to think about all the ways you can protect your devices, from using a firewall to consistently monitoring your network for suspicious activity. Adopting this kind of mindset will make you a tough match against the tricks cybercriminals have up their sleeves.
Frequently asked questions
Keep reading for answers to frequently asked questions regarding password security.
What is password security?
Password security involves using cybersecurity tools, best practices, and procedures to create passwords that can better protect personal information.
Why is password security important?
Creating a secure password is the first step a person can take to safeguard their personal devices and information.
What are the safest types of passwords?
The best types of passwords include a wide variety of numbers and characters with a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters. They shouldn't reference personal information, such as names, addresses, or phone numbers.
How do I make my password secure?
Follow these five tips for creating a secure password:
- Never use personal information.
- Include a combination of letters, numbers, and characters.
- Prioritize password length.
- Never repeat passwords.
- Avoid using real words.
What is an example of a secure password?
A strong password includes a mix of numbers, symbols, and letters while also prioritizing length.
An example of a secure password would be: Wb%liYrLVNip*7lv
What are the five most common passwords?
The five most common passwords used today include:
- 123456
- 123456789
- qwerty
- password
- 12345
How do hackers get your password?
There are a number of ways hackers can get ahold of your password. Some methods hackers commonly use include credential stuffing, password spraying, keylogging, phishing scams, and dictionary attacks.
Does changing your password stop hackers?
Yes, changing your password can prevent hackers from getting their hands on your sensitive information.
Can a password be attacked by brute force?
Yes, some passwords are susceptible to brute force techniques. Credential stuffing, password spraying, and dictionary attacks are common methods seen on the internet.
Can a password be dictionary attacked?
Yes, passwords using one single word are susceptible to dictionary attacks. Using a complex password with a variety of letters, numbers, and characters is a quick solution.

Cyber threats have evolved, and so have we.
Norton 360™ with LifeLock™, all-in-one, comprehensive protection against viruses, malware, identity theft, online tracking and much, much more.
Try Norton 360 with Lifelock.
Editorial note: Our articles provide educational information for you. Our offerings may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc.

Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.